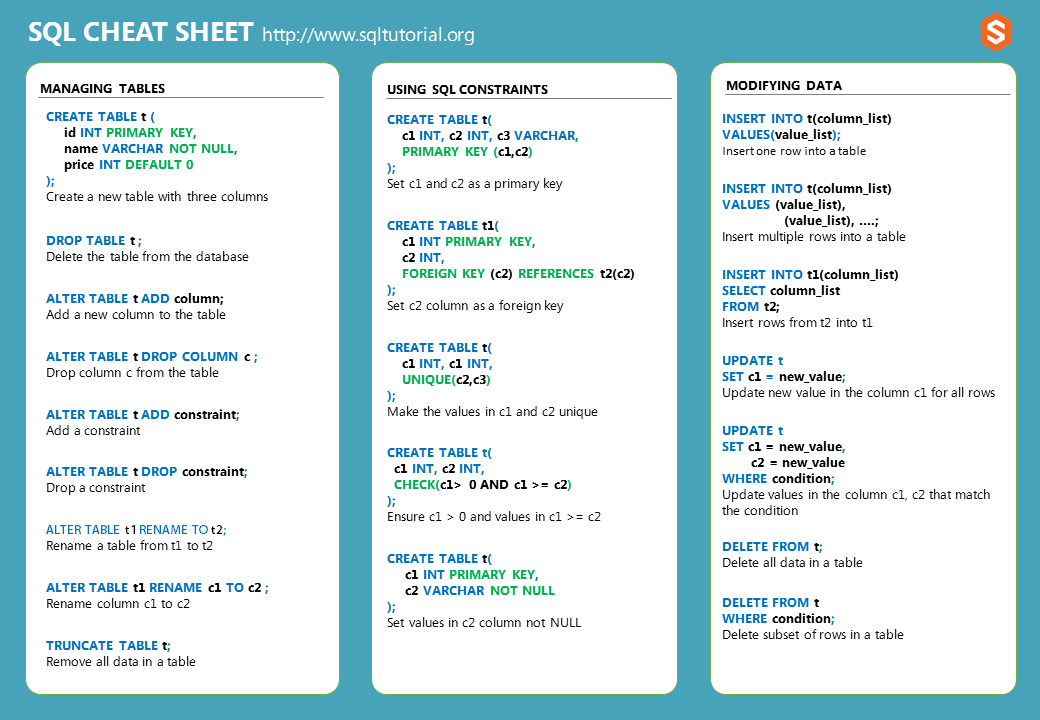
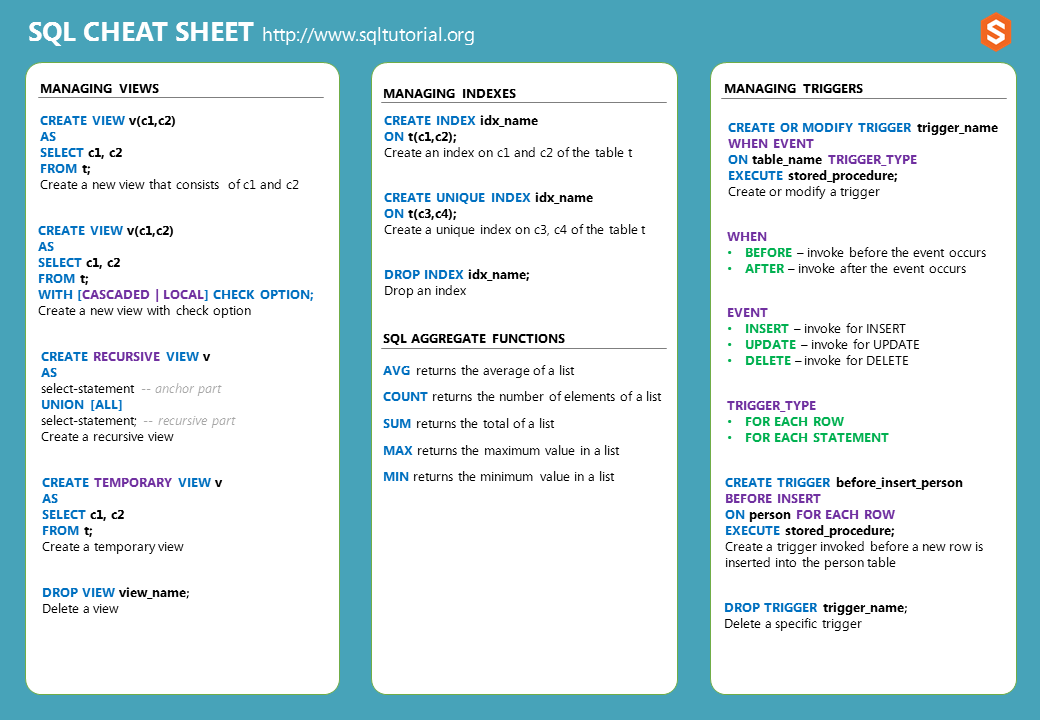
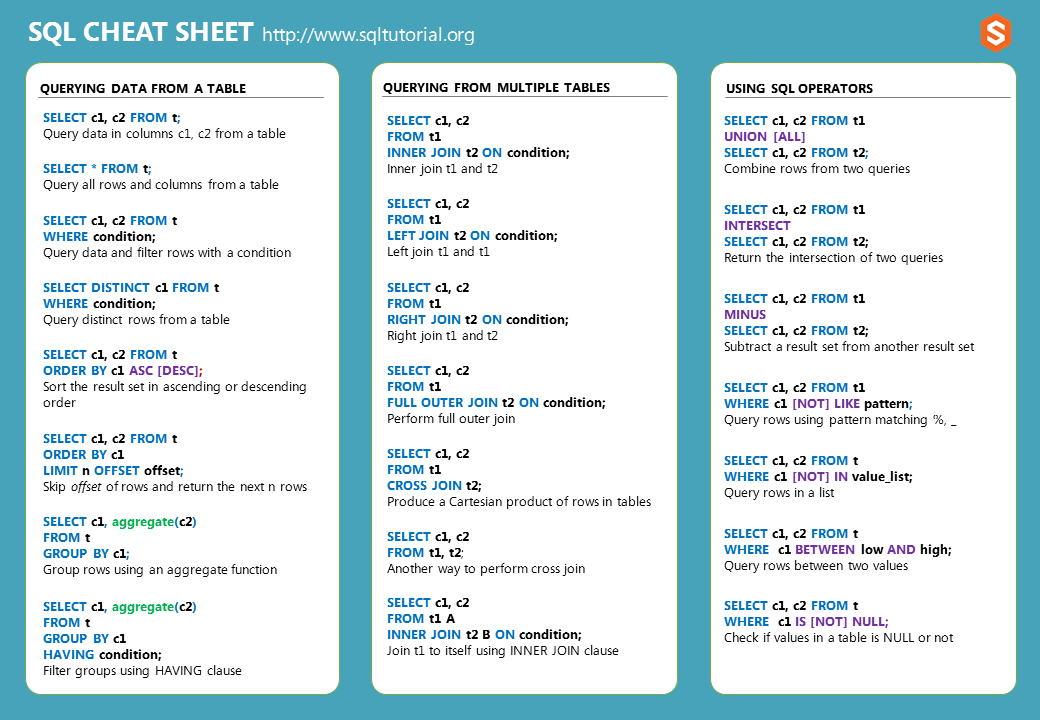
The SQL cheat sheet provides you with the most commonly used SQL statements for your reference. You can download the SQL cheat sheet as follows:
Download the 3-page SQL cheat sheet in PDF format

 #
#
Querying data from a table #
Query data of column1 and column2 from a table:
SELECT
column1,
column2
FROM
table_name;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Query all data from a table:
SELECT
*
FROM
table_name;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Retrieve specific rows based on a condition:
SELECT
column1,
column2
FROM
table_name
WHERE
condition;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Query distinct rows from the column1 and column2 from a table:
SELECT DISTINCT
column1,
column2
FROM
table_name;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Sort the result set in ascending order:
SELECT
column1,
column2
FROM
table_name
ORDER BY
column1;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Sort the result set in descending order:
SELECT
column1,
column2
FROM
table_name
ORDER BY
column2 DESC;Skip m rows before returning the next n rows from a table:
SELECT
column1,
column2
FROM
table_name
ORDER BY
column1
LIMIT
n
OFFSET
m;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Group rows and apply an aggregate function to each group:
SELECT
column1,
aggregate_fn (column2)
FROM
table_name
GROUP BY
column1;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Filter groups by a condition using HAVING clause:
SELECT
column1,
aggregate_fn (column2)
FROM
table_name
GROUP BY
column1
HAVING
condition;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Querying data from multiple tables #
Perform an inner join of two tables:
SELECT
column1,
column2
FROM
table1
INNER JOIN table2 ON condition;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Perform a left join of two tables:
SELECT
column1,
column2
FROM
table1
LEFT JOIN table2 ON condition;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Perform a right join of two tables:
SELECT
column1,
column2
FROM
table1
RIGHT JOIN table2 ON condition;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Perform a full outer join:
SELECT
column1,
column2
FROM
table1
FULL OUTER JOIN table2 ON condition;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Perform a cross-join:
SELECT
column1,
column2
FROM
table1
CROSS JOIN table2;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Perform a self-join using an inner join:
SELECT t1.column1, t2.column2
FROM table1 t1
INNER JOIN table1 t2 ON condition;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Set operations #
Return the union of two result sets:
SELECT column1, column2
FROM table1
UNION [ALL]
SELECT column1, column2
FROM table2;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Return the intersection of two result sets:
SELECT column1, column2
FROM table1
INTERSECT [ALL]
SELECT column1, column2
FROM table2;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Subtract a result set from another result set:
SELECT column1, column2
FROM table1
MINUS
SELECT column1, column2
FROM table2;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Logical operators #
Query rows using pattern matching:
SELECT column1, column2
FROM table_name
WHERE column1 [NOT] LIKE pattern;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Check if a value in a set of values:
SELECT column1, column2
FROM table_name
WHERE column1 [NOT] IN (v1, v2, v3);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Check if a value is in a range of values:
SELECT column1, column2
FROM table_name
WHERE column1 [NOT] BETWEEN low AND high;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Check if a value is NULL or not:
SELECT column1, column2
FROM table_name
WHERE column1 IS [NOT] NULL;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Managing tables #
Create a new table:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS table_name (
column1 datatype PRIMARY KEY,
column2 datatype constraint,
table_constraint
);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Remove a table from the database:
DROP IF EXISTS TABLE table_name ;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Add a new column to the table:
ALTER TABLE table_name
ADD column1 datatype constraint;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Drop a column from the table:
ALTER TABLE table_name
DROP COLUMN column1;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Add a constraint:
ALTER TABLE table_name
ADD constraint;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Drop a constraint:
ALTER TABLE table_name
DROP constraint;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Rename a table:
ALTER TABLE table1
RENAME TO table2;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Rename a column:
ALTER TABLE table1
RENAME column1 TO column2;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Remove all data from a table fast:
TRUNCATE TABLE table_name;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Using SQL constraints #
Create a composite primary key:
CREATE TABLE table_name (
column1 datatype,
column2 datatype,
column3 datatype,
PRIMARY KEY (column1, column2)
);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Create a foreign key constraint:
CREATE TABLE table_name (
column1 datatype PRIMARY KEY,
column2 datatype,
FOREIGN KEY (column2) REFERENCES table2(column2) ON DELETE CASCADE ON UPDATE CASCADE
);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Create a unique constraint that includes two columns:
CREATE TABLE table_name (
column1 data_type,
column2 data_type,
column3 data_type,
UNIQUE(column2,column3)
);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Create a CHECK constraint:
CREATE TABLE table_name (
column1 datatype,
column2 datatype,
CHECK(expression)
);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Set a NOT NULL constraint:
CREATE TABLE table_name (
column1 datatype,
column2 datatype NOT NULL
);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Modifying Data #
Insert one row into a table:
INSERT INTO table_name(column_list)
VALUES(value_list);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Insert multiple rows into a table:
INSERT INTO table_name(column_list)
VALUES (value_list),
(value_list);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Insert data selected from the table2 into table1:
INSERT INTO table1(column_list)
SELECT column_list
FROM table2;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Update the new value in the column for all rows:
UPDATE table_name
SET column1 = new_value;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Update values in two columns in rows that match the condition:
UPDATE table_name
SET column1 = new_value,
column2 = new_value
WHERE condition;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Delete all data in a table:
DELETE FROM table_name;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Delete a subset of rows in a table:
DELETE FROM table_name
WHERE condition;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Managing Views #
Create a new view based on a query:
CREATE VIEW view_name(column1,column2)
AS
query;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Create a new view with the WITH CHECK OPTION:
CREATE VIEW view_name(column1, column2)
AS
query
WITH [CASCADED | LOCAL] CHECK OPTION;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Create a recursive view:
CREATE RECURSIVE VIEW view_name
AS
query -- anchor part
UNION [ALL]
query; -- recursive partCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Create a temporary view:
CREATE TEMPORARY VIEW view_name
AS
query;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Delete a view:
DROP VIEW IF EXISTS view_name;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Managing indexes #
Create an index on column1 and column2 of the table table_name:
CREATE INDEX index_name
ON table_name(column1,column2);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Create a unique index on column3 and column4 of the table_name:
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX index_name
ON table_name(column3, column4)Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Drop an index:
DROP INDEX index_name;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Managing triggers #
Create or replace a trigger:
CREATE OR MODIFY TRIGGER trigger_name
WHEN EVENT
ON table_name TRIGGER_TYPE
EXECUTE stored_procedure;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Delete a specific trigger:
DROP TRIGGER trigger_name;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)