Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the SQL LAST_VALUE() function to return the last value in an ordered set of values.
Overview of LAST_VALUE() Function
The LAST_VALUE() is a window function that returns the last value in an ordered set of values.
The following illustrates the syntax of the LAST_VALUE() function:
LAST_VALUE(expression) OVER (
partition_clause
order_clause
frame_clause
)
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this syntax:
expression
The returned value of the function which can be a column or an expression that results in a single value.
The OVER clause consists of three clauses: partition_clause, order_clause, and frame_clause.
partition_clause
The syntax of the partition_clause clause is as follows:
PARTITION BY expr1, expr2, ...
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The PARTITION BY clause divides the rows of the result sets into partitions to which the LAST_VALUE() function applies. Because the PARTITION BY clause is optional, if you omit it, the function treats the whole result set as a single partition.
order_clause
The order_clause clause specified the order of rows in partitions to which the LAST_VALUE() function applies. The syntax of the ORDER BY clause is as follows:
ORDER BY expr1 [ASC | DESC], expr2, ...
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)frame_clause
The frame_clause defines the subset (or frame) of the partition being evaluated. For the detailed information on the frame clause, check it out the window function tutorial.
SQL LAST_VALUE() function examples
We will use the following employees and departments tables from the sample database for demonstration.
A) Using SQL LAST_VALUE() function over result set example
The following statement finds employees who have the highest salary in the company:
SELECT
first_name,
last_name,
salary,
LAST_VALUE (first_name) OVER (
ORDER BY salary
RANGE BETWEEN UNBOUNDED PRECEDING AND
UNBOUNDED FOLLOWING
) highest_salary
FROM
employees;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the partial output:
In this example, the ORDER BY clause sorted employees by salary and the LAST_VALUE() selected the first name of the employee who has the lowest salary.
The frame clause is as follows:
RANGE BETWEEN UNBOUNDED PRECEDING AND UNBOUNDED FOLLOWING
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)It means the frame starts at the first row (UNBOUNDED PRECEDING) and ends at the last row ( UNBOUNDED FOLLOWING) of the result set.
B) Using SQL LAST_VALUE() over partition example
The following statement finds employees who have the highest salary in each department.
SELECT
first_name,
last_name,
department_name,
salary,
LAST_VALUE (CONCAT(first_name,' ',last_name)) OVER (
PARTITION BY department_name
ORDER BY salary
RANGE BETWEEN UNBOUNDED PRECEDING AND
UNBOUNDED FOLLOWING
) highest_salary
FROM
employees e
INNER JOIN departments d
ON d.department_id = e.department_id;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The following picture shows the output of the query:
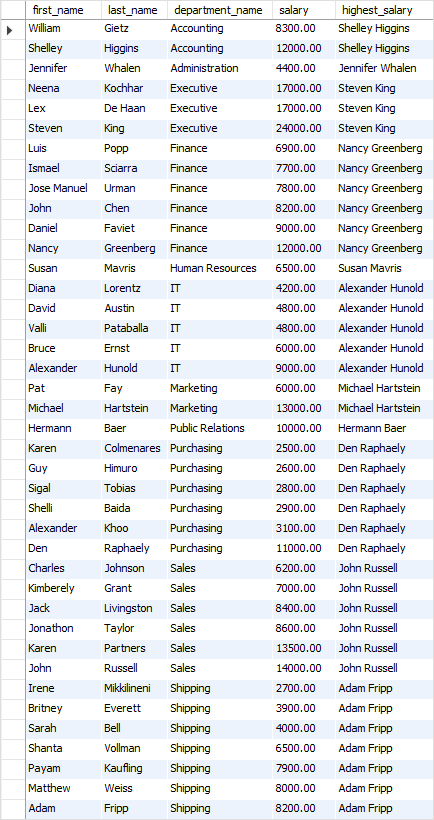
Let’s examine the query in more detail:
- First, the
PARTITION BYclause divided the employees by departments. - Then, the
ORDER BYclause sorted employees in each department by their salary in ascending order. - Finally, the
LAST_VALUE()is applied to sorted rows in each partition. Because the frame starts at the first row and ends at the last row of each partition, theLAST_VALUE()selected the employee who has the highest salary.
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the SQL LAST_VALUE() function to get last value in an ordered set of values.